
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 : Why Study In Germany
1. How is the Education System in Germany?
2. What are the benefits of studying in Germany? Why Study in Germany?
3. Is it tough to get admission in German universities?
4. Factors to consider while choosing Universities in Germany
5. Is tuition fees in Germany free for foreign students? How Much Does it Cost to Study in Germany?
6. Do the German universities give really good placements?
7. Is it better to do an MS in the US or an MS in Germany?
8. Which is better for International students: Canada or Germany?
Chapter 2 : Application & Student VISA Process
1. How to Apply for German Universities?
2. What are the application deadlines for German universities (Summer and Winter)?
3. What is the ideal time to apply for masters in Germany?
4. Can I do my studies in Germany after my 12th? Do german universities accept SAT for international students?
5. Germany study visa requirements for International students
6. How difficult is it to get a German Student Visa?
7. Can I study in germany on a job visa?
8. What score in tests (Ielts etc.,) is required for a German study visa?
9. How Much Does It Cost to Apply for a German Visa?
Chapter 3 : Top Universities & Admission Reuirements
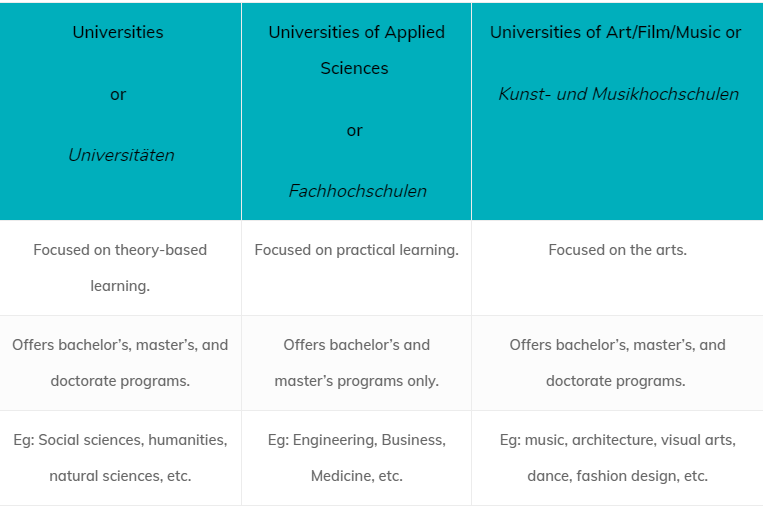
1. What’s the difference between a university and a Fachhochschulen?
2. What are the best universities in Germany for masters /Ph.D?
3. Which are the best universities for engineering in Germany?
4. Which are the top German Universities for MBA?
5. Which universities in Germany offer free study?
6. Which is the easiest German university to get admission into?
7. What are the requirements to study in Germany?
8. Is GRE and IELTS or TOEFL mandatory for master’s programs in Germany? – Can I study in Germany without the IELTS?
9. What is the minimum CGPA required for MS in Germany?
10. Is German language mandatory to study in German universities?
11. How much funds are required to study a master’s in Germany?
12. Is work experience necessary for an MS in Germany?
Chapter 4 : Life in Germany for International Students
1. What is it like to study in Germany for foreign students?
2. What is it like to study at a German university or college? What are the pros and cons of living in Germany?
3. What about the part-time jobs in Germany?
4. How is life in Germany different from the US?
5. What are the employment opportunities in Germany? How do you go about finding a job while you are studying?
6. What jobs can I seek as an international student?
7. What are the transportation options in Germany for international students?
1) How is the Education System in Germany?/ What are the types of universities in Germany?
2. What are the benefits of studying in Germany? Why Study in Germany?
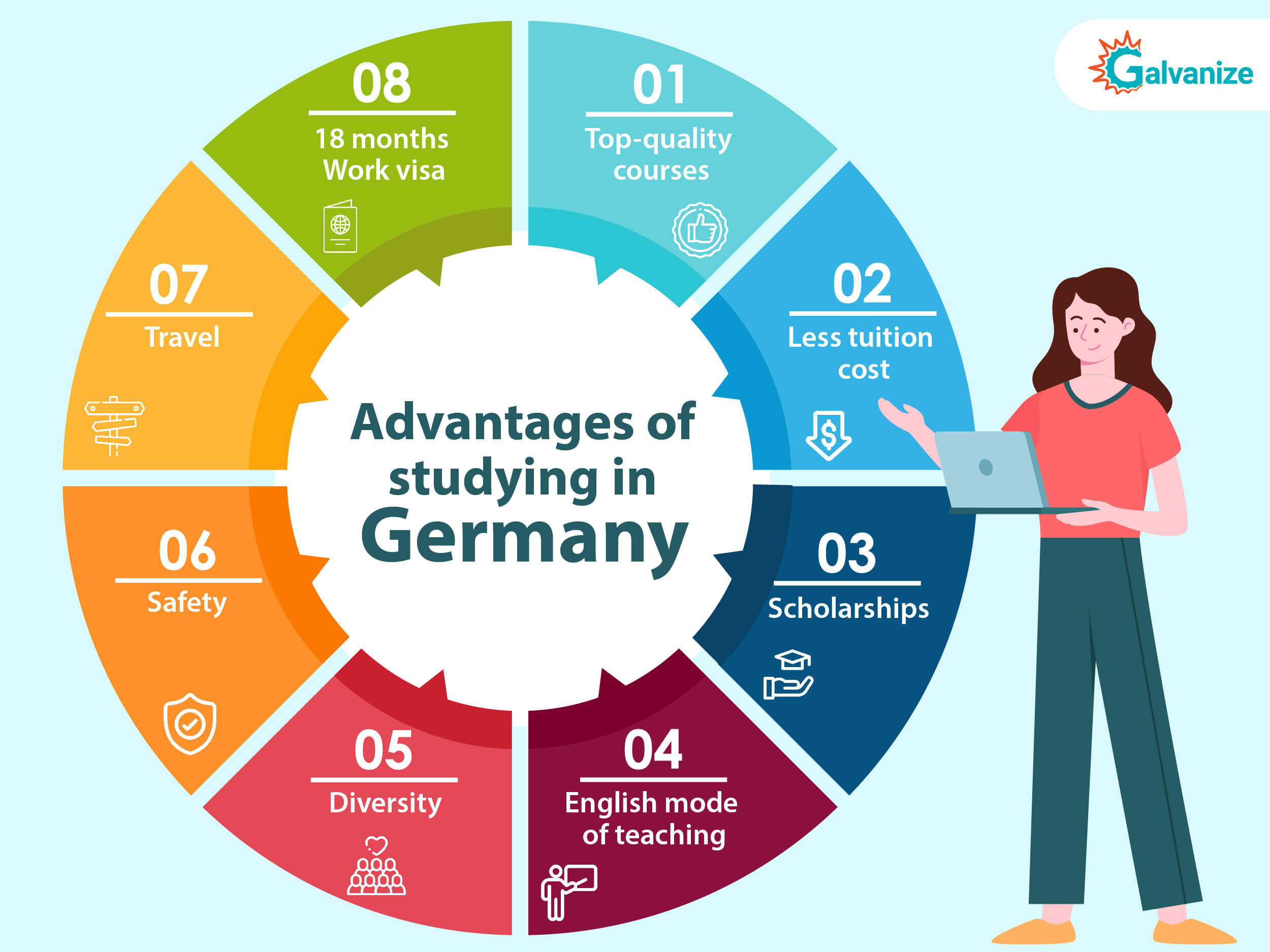
There are several reasons that make Germany the ideal country of study for international students:
1.Top-quality courses:
German universities are known for their high standard of education and students can be rest assured that they will be trained to meet the highest standard of academic excellence.
2. Less tuition cost:
Public universities or state-run universities do not charge native or international students any tuition fee, so students pay only a small fee towards administrative and service costs. Tuition fees are charged for non-consecutive Master’s degree courses. The amount of tuition fees varies individually.
3. Scholarships:
German universities offer several scholarships to deserving meritorious international students under the DAAD – the German Academic Exchange Service.
4. English mode of teaching:
Though Germany is not an English-speaking country, the universities do provide many programs that are taught in English.
5. Diversity:
Students come from all across the globe to study in Germany. As such, there is a rich, diverse culture in the country, and international students can rest assured that there is a place for everyone.
6. Safety:
Germany is known to be comparatively safer than other countries, and since the country maintains political-economic stability, it is an ideal place for international students. Moreover, Germany has one of the best health care systems in the world
7. Travel:
If traveling is something you like to do or something you’ve always had on your bucket list, then Germany is the perfect place. Your student ID, or your public transport pass which is usually included in your semester fees, allows you free usage of the public transport in your region. Moreover, as Germany is closely bordered by so many other European countries, it is cheaper and less time-consuming to travel for a weekend away to one of these beautiful countries.
8. 18 months Work visa:
For students who hail from countries outside of the EU, a period of 18 months after graduation is granted to them to find employment or prepare for further education. However, you will need to apply to extend your residence permit if you wish to continue living in the country. Once you’ve found employment, you can apply for a German residence permit or an EU Blue Card.
3. Is it tough to get admission in German universities?
As Germany is one of the few countries that offer tuition-free study, competition is increasing every year. Students from all over the world apply to German universities, attracted to the high quality of teaching at a low cost. But since German admission committees place a lot of weight-age on grades of previous studies, if you have high grades and achievements, you have a good chance of getting into one of the top universities.
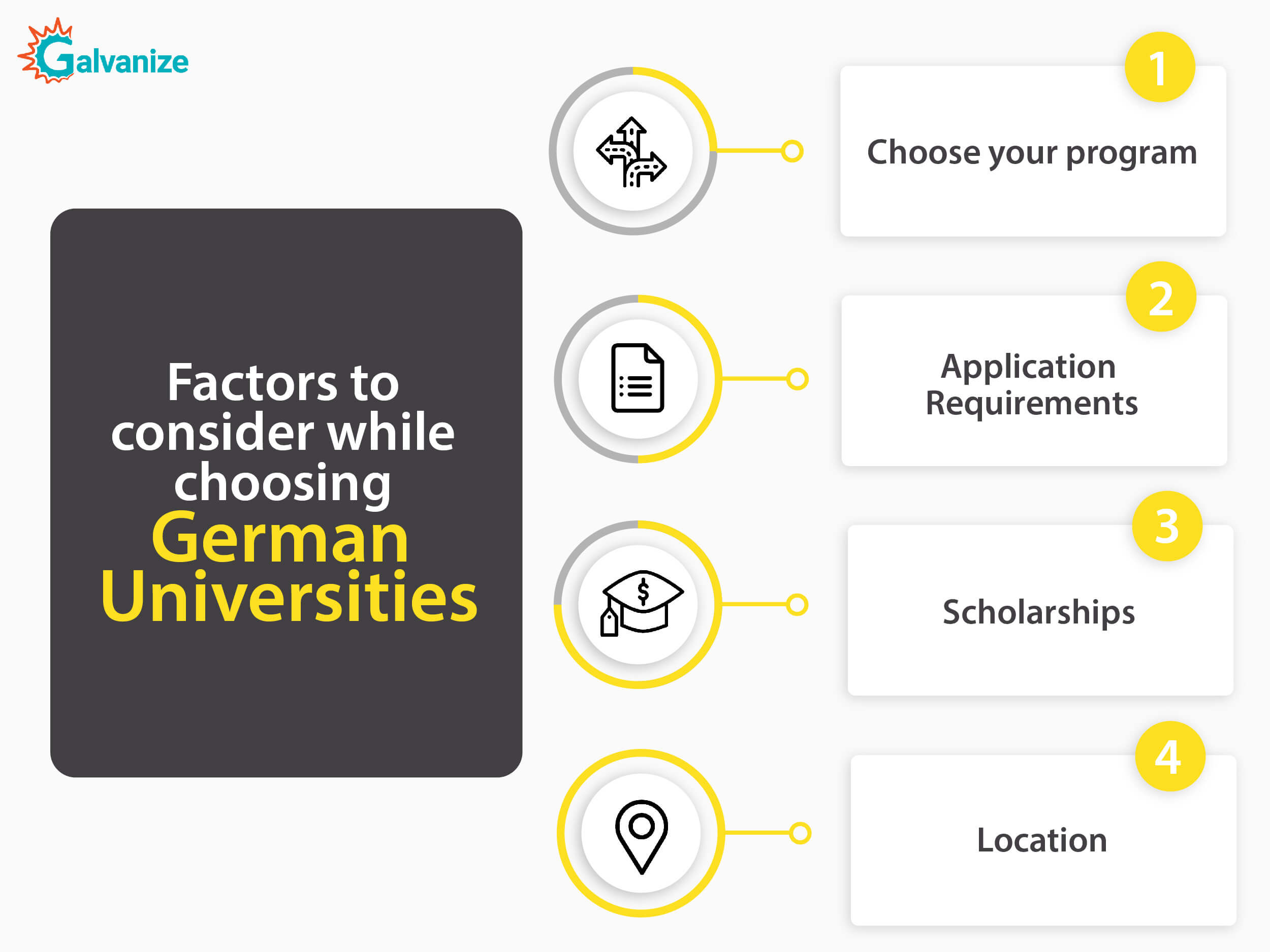
4. Factors to consider while choosing Universities in Germany
Choose your program:
Firstly, you need to decide what kind of program you are looking for. You will need to decide whether you are going for a more theory focused program or an applied practical program. You can narrow down your university choice by deciding between Universitäten, Fachhochschulen, and Kunst- und Musikhochschulen.
Application Requirements:
Once you’ve decided on the program, you need to check the application requirements. Many of the major courses in Germany have standard requirements across all universities, so you should check out what the requirements of your target program are. Also, due to the highly competitive environment, some German programs place restrictions on the number of students who can enroll. Make sure to check these details before applying to a program.
Scholarships:
German universities provide several scholarships for international students under the DAAD. Check which ones you are eligible for and apply. You could also check the university’s website for eligibility for scholarships.
Location:
Germany as a whole is a beautiful country. But of course, like most countries, some places are more populated than others. You might prefer studying in a major city like Munich or Hamburg with a large student population. Or maybe you prefer a small, tightly-knit town, Heidelberg, where it is easier to find affordable accommodation. Whichever you choose, don’t compromise on your preferred course of study.
5. Is tuition fees in Germany free for foreign students? How Much Does it Cost to Study in Germany?
Germans believe that education should be free to all, and not commercialized. Moreover, the attraction of free education encourages more Germans to opt for higher education, while also attracting the best minds from across the world to study in the country. The economic and social benefits of offering free education are huge, and as such, public/state-run universities in Germany do not charge tuition fees.
State financed universities in Germany do not charge a tuition fee for EU or non-EU students attending Bachelor’s programs or consecutive Master’s programs. A consecutive Master’s program builds on a previously completed bachelor’s program in the same field allowing students to deepen and broaden the knowledge and skills previously acquired.
You have to complete an undergraduate degree in a specified field to qualify for admission.
Non-consecutive Master’s programs means that the Bachelor’s degree is in a different field than the Master’s degree sought, e.g. MBA programs. Typically there is a tuition cost associated with Non-consecutive Master’s programs.
All programs will require students to pay a small fee for administration costs. While a majority of students attend state-run universities, there is also a minority who attend private colleges. The tuition at private universities is understandably higher, but the quality of education is the same.
|
Average Monthly Living expenses |
|
|
Rent and utilities |
€323 |
|
Food and drink |
€168 |
|
Clothing |
€42 |
|
Working/learning materials |
€20 |
|
Travel costs (car and public transport) |
€94 |
|
Health insurance, medical costs, medicine |
€80 |
|
Phone, internet, TV |
€31 |
|
Leisure, culture, sports |
€61 |
|
Total |
€819 |
6. Do the German universities give really good placements?
As Germany has the largest economy in Europe, there are a lot of job opportunities available. Most universities have career centers to help students find employment opportunities. However, the competition for these positions is quite high, so students should begin applying to companies as soon as their final year begins. Moreover, most companies require employees to speak German, so if you are planning on working in the country after your studies, you might want to consider learning German.
Students are granted an extended period of 18 months after their final exam results are announced to search for a job. If you wish to apply for this extended work permit, you should apply, proving that you have health insurance and are able to support yourself financially. However, do not wait until this period to begin searching for opportunities. Plan ahead.
7. Is it better to do an MS in the US or an MS in Germany?
|
MS in USA |
MS in Germany |
|---|---|
|
Tuition costs are very high. |
Tuition is free or costs are negligible. |
|
Popular courses to study are: Engineering, Business, IT and allied fields, Sports, Nutritional Science, Computer Science, English Literature, Physiotherapy, Hospitality. |
Popular courses are: Automobile Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Computer Science Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Physics, Life Sciences. |
|
Living and accommodation costs in the US are expensive. |
Living and accommodation costs are comparatively cheaper in Germany. |
|
Weather varies, depending on the region - some are warm and some are cold. |
Weather changes drastically and can be unpredictable. |
|
Culture is very diverse, as students from all across the world come to study in the US. Language is not a problem either. |
Language can be a problem, even among a diverse community. You need to consider learning German. |
|
Difficult to find a technical part-time job, especially one off-campus. |
It is relatively easier to find a technical part-time job, especially off-campus |
|
MS programs can have a duration of 1-3 years. |
MS programs tend to be only a year-long. |
|
You can apply to most graduate programs only if you have completed 12 years of schooling with 4 years of undergraduate study. |
Many universities accept students who have completed only 15 years of study. |
|
If you opt for post-completion OPT you can stay in the US for 12 months after graduation and work part-time or full-time. |
You can request an extension to your residence permit and stay in Germany for up to 18 months after graduation, to search for a job or further study options. |
8. Which is better for International students: Canada or Germany?
|
Canada |
Germany |
|---|---|
|
|
Chapter 2 : How to apply for German Universities | Application Deadlines & Processes
Table of Contents
1. How to Apply for German Universities?
2. What are the application deadlines for German universities (Summer and Winter)?
3. What is the ideal time to apply for masters in Germany?
4. Can I do my studies in Germany after my 12th? Do german universities accept SAT for international students?
5. Germany study visa requirements for International students
6. How difficult is it to get a German Student Visa?
7. Can I study in germany on a job visa?
8. What score in tests (Ielts etc.,) is required for a German study visa?
9. How Much Does It Cost to Apply for a German Visa?
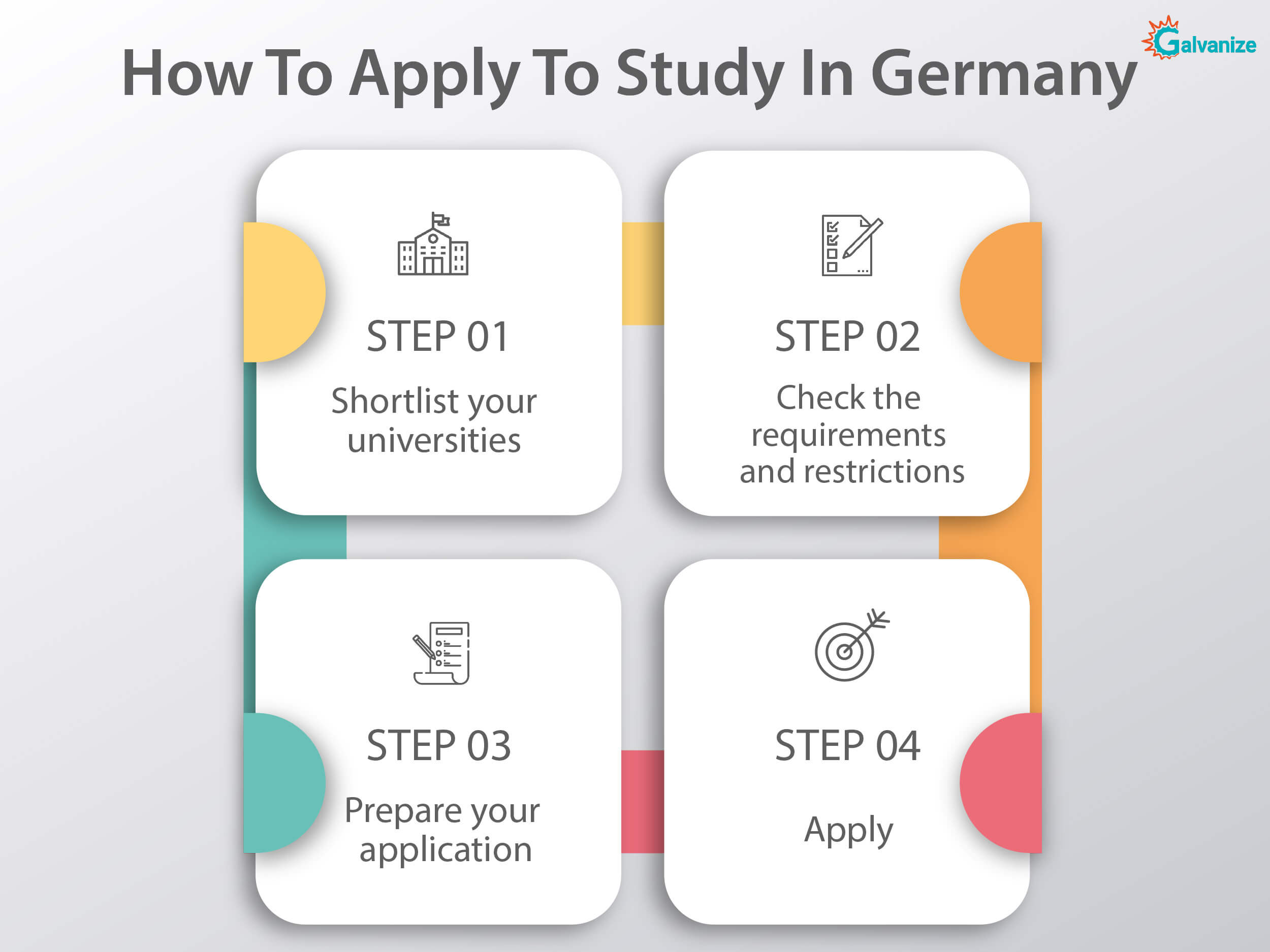
1) How to Apply for German Universities? | Applying for German Universities
1. Shortlist your universities:
Decide on which program you wish to apply for and which universities you would like to study in. Keep in mind that German universities pride themselves on maintaining the highest standards of education in all their universities, so make your pick depending on how best a particular program would suit your professional goals.
2. Check the requirements and restrictions:
Some programs, especially those which are in high demand, such as medicine, dentistry and pharmacy, have a strictly regulated admissions process. This regulation could be local (only applying to particular universities) or nationwide (applying to universities all across the country). This is because of the high competition for getting into these programs. As such, universities often require students to meet a particular cut-off grade of their previous course of study, attend a selection interview or pass an exam.
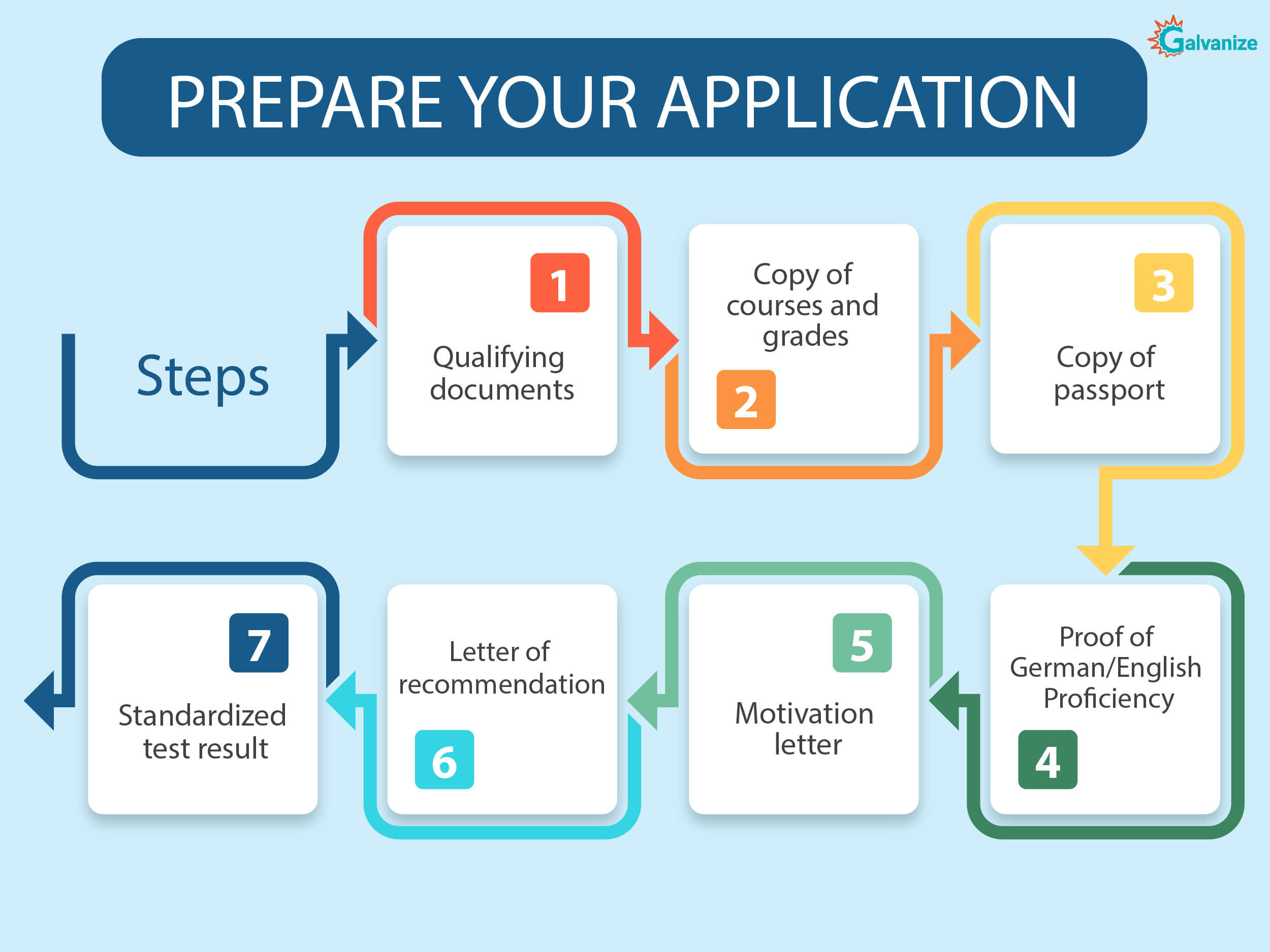
3. Prepare your application:
The German university application process generally requires the following documents, though specific universities might require additional paperwork.
-
- High school diploma, college transcript, or a similar qualifying document that verifies your previous course of study.
- A translated copy of your courses and grades.
- Passport copy and passport-sized photograph.
- Proof of your German/English proficiency (depending on which language you are taking the course in).
- Motivation letter, which is a letter describing your motivation, or your reason for choosing to study a particular course in a specific university.
- Letters of recommendation
- Standardized test results, such as the GMAT or GRE, or some other additional entrance test results.
4. Apply:
Once you’ve gathered all your documents and have your financial details in order, you can apply. Check the deadline for your applications, and try to submit as early as possible.
2. What are the application deadlines for German universities (Summer and Winter)?
The specific deadlines differ from university to university. But these are the deadlines followed by most universities:
Summer Deadline: 15th January
Summer Semester Begins: March – April
- This date is the extended deadline, but you should try to get your application in by December at the latest. This not only priortizes your application for admission, but also for scholarships.
Winter Deadline: 15th July
Winter Semester Begins: September – October
- Once again, this is the extended deadline. A lot of universities close their application portals in May/June, so make sure you check the application deadlines for your specific university before applying.
Also, keep in mind that you might need to send the hard copies of your documents after applying online. These hard copies need to reach the university before the application deadline, even if your online application was filled beforehand. Hence, make sure you give plenty of time for postal delays and other unpredictable factors.
3) What is the ideal time to apply for masters in Germany?
There is no ideal time to apply. German universities have two intakes – Summer and Winter. The Summer deadline is 15th January, but you should focus on getting your application in by December at the latest. If you choose the Winter Deadline, though the extended deadline grants you time till 15th July, it would be best if you submit your application by May or June. Submitting your application earlier will not only give the admission committee plenty of time to review your application, but it will also prioritize your application for scholarships, housing, and other factors.
So, other than submitting your application as early as possible, the ideal intake comes down to which time is most suitable for you.
4) Can I do my studies in Germany after my 12th? Do German universities accept SAT for international students?
Yes, you can, provided that you meet the eligibility criteria.
To attend an undergraduate degree at a German university, you will need a “university entrance qualification.” If your secondary school-leaving certificate is not recognised in Germany, you should complete a foundation course (“Studienkolleg”) in Germany. These foundation courses have their own entrance exams and German language proficiency requirements. At the conclusion of the foundation course, you will be tested in several subjects relevant to your intended program of study at the university. This test is called the “university entrance assessment examination” (“Feststellungsprüfung”). One part of the examination is a language test. This course usually lasts for about two semesters with preparatory courses with specific specializations relevant to your field of study. The final exam not only proves your proficiency in these fundamental concepts, but also your ability to handle college-level classes. Upon successful completion of this assessment, you may apply to attend a university.
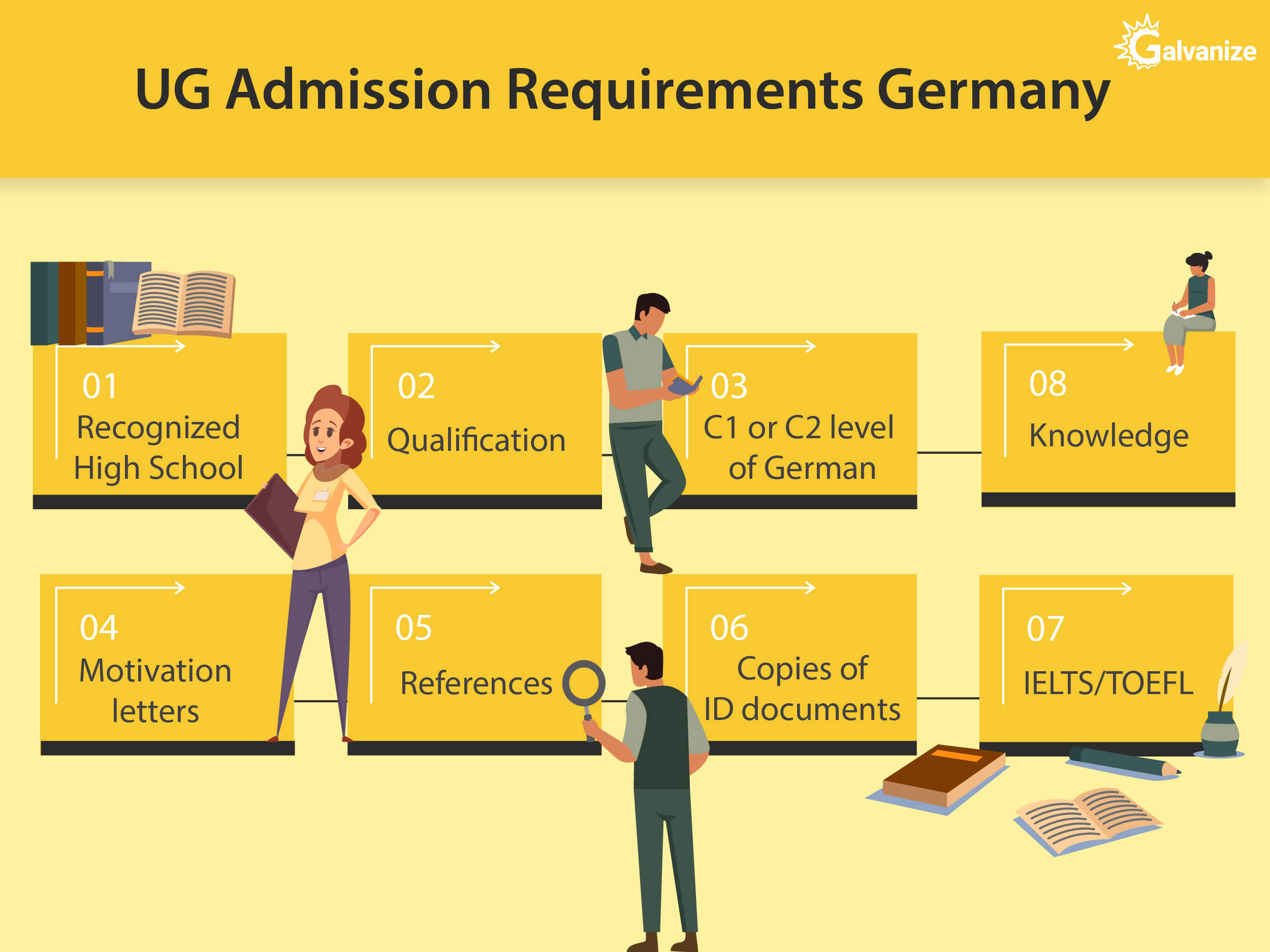
German universities do not require the SAT for Undergraduate admissions. However to pursue a BS, BA or B.Engg. in Germany, students will have to meet the following admissions requirements:
- High School qualifications recognized by German Universities
- If your High School qualifications are not recognized, a foundation course must be completed
- Most undergraduate courses at German universities are taught in German language. You have to prove German language knowledge of level C1 or C2 of the “Common European framework of references for languages”. If you cannot learn enough German at school, contact Goethe Institute
- Motivation Letters
- References
- Copies of ID documents
- IELTS/TOEFL maybe recommended based on your program requirements
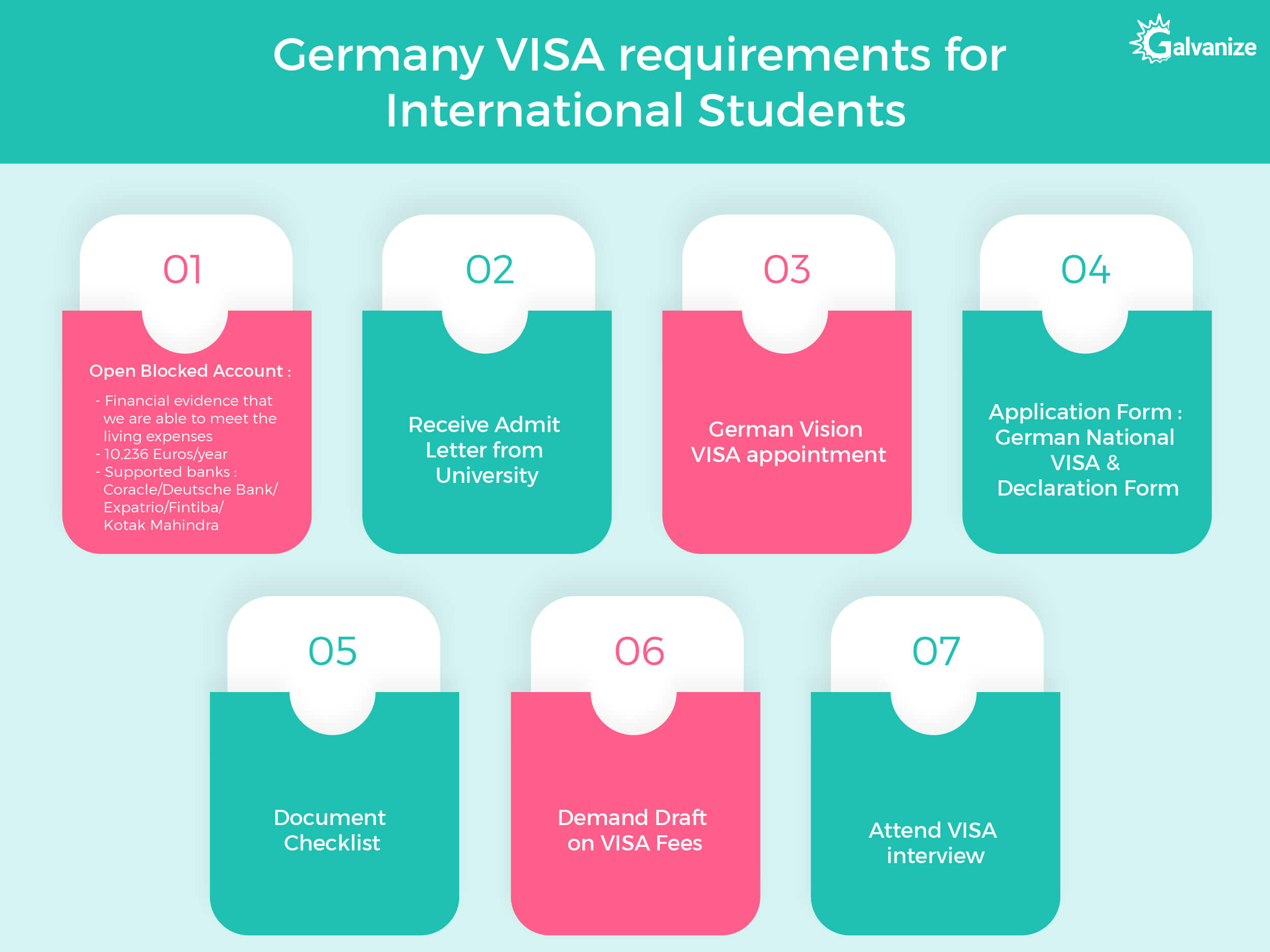
5. Germany study visa requirements for International students
The German Mission in India clearly outlines the stepsfor procuring a German National visa required to pursue higher studies in Germany. Following are the most important elements of securing a German National Visa
- Open Blocked account:
- Provide evidence that you are able to meet your living costs by opening a blocked bank account.
-
- Amount – 853 Euros for one month/ 10236 Euros for one year
- Coracle/Deutsche Bank/Expatrio/Fintiba/Kotak Mahindra
- Receive admit letter from German University
- Be aware of the German mission visa appointment booking procedures since wait times can be long, as restrictions apply on location based on place of residence
- Fill out the Application form for – German National Visa and Declaration form. Print them out, sign it and submit along with the other documents.
Carry all documents listed in the checklist
- Prepare Demand Draft for visa fees based on specifications
- Attend the visa interview
6. How difficult is it to get a German Student Visa? What is the student visa processing time for Germany?
The process to secure a German National Visa for higher studies can be an arduous and time consuming task. From opening the blocked account, to preparing the documents and scheduling a visa appointment, the process can be very time consuming and students are advised to apply at least 3 months in advance of their intended travel.
7. Can I study in Germany on a job visa?
To study in Germany with the full benefits of an international student, one must have a student visa.
8. What score in tests (Ielts etc.,) is required for a German study visa?
To apply for university studies taught in English language, students will typically require an English Proficiency test – TOEFL/IELTS. German Language proficiency may be required by some programs. GMAT and GRE are becoming increasingly important, especially for Economics and business courses.
9. How Much Does It Cost to Apply for a German Visa?
If applying for a German National Visa in India, the visa fee is 75 Euros and should be paid as a demand draft at the end of the visa interview.

Chapter 3 : Top Universities & Admission Requirements
Table of Contents
1. What’s the difference between a university and a Fachhochschulen?
2. What are the best universities in Germany for masters /Ph.D?
3. Which are the best universities for engineering in Germany?
4. Which are the top German Universities for MBA?
5. Which universities in Germany offer free study?
6. Which is the easiest German university to get admission into?
7. What are the requirements to study in Germany?
8. Is GRE and IELTS or TOEFL mandatory for master’s programs in Germany? – Can I study in Germany without the IELTS?
9. What is the minimum CGPA required for MS in Germany?
10. Is German language mandatory to study in German universities?
11. How much funds are required to study a master’s in Germany?
12. Is work experience necessary for an MS in Germany?
1) What’s the difference between a university and a Fachhochschulen?
University or Universitäten in Germany are mostly focused on theoretical education, as compared to applied learning. Fachhochschulen, on the other hand, offers courses that are centered around practical learning, such as Colleges of engineering, business, and medicine. Another difference between the two is that though both categories of institutions offer bachelor’s and master’s programs, only Universitäten are authorized to offer doctorate programs.
However, the current scenario is changing, as many Universitäten are including practical modules into their courses, and some Fachhochschulen has been allowed to offer doctoral programs. Be sure to do your research before choosing a university.
2. What are the best universities in Germany for masters/Ph.D.?
According to the Times Higher Education ranking, these are the top universities in Germany in 2020:
- LMU Munich
- Technical University of Munich
- Heidelberg University
- Humboldt University of Berlin
- Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
- University of Freiburg
- University of Tübingen
- RWTH Aachen University
- University of Bonn
- Free University of Berlin
3. Which are the top German Universities for MBA?
The top 5 German universities as ranked by QS Top MBA are:
- Mannheim Business School
- Frankfurt School of Finance and Management
- WHU – Otto Beisheim School of Management
- ESMT Berlin
- HHL Leipzig Graduate School of Management
4. Which are the best universities for engineering in Germany?
According to the US News and World Report, the top 10 best engineering universities in Germany are:
- Technical University of Munich
- RWTH Aachen University
- Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
- Technical University of Berlin
- University of Duisburg-Essen
- University of Stuttgart
- Darmstadt University of Technology
- Technical University of Dresden
- University of Erlangen Nuremberg
- University of Freiburg
5. Which universities in Germany offer free study?
The World Scholarship Forum has listed the following universities as those that offer free tuition:
- Ludwig Maximilian University, Munich
- Ruprecht-Karls-universität Heidelberg (Heidelberg University)
- Humboldt University of berlin
- Freie universität berlin (free university of berlin)
- Georg-august-universität göttingen (university of göttingen)
- University of Hamburg
- University of Stuttgart
- Technische universität münchen
- Kit, Karlsruhe Institut für Technologie
- Rwth Aachen university
- Technische universität berlin (Tu berlin)
- Eberhard Karls universität tübingen
- Albert-Ludwigs-Universitaet Freiburg
- University of Bremen
- Hasso-Plattner-inst. Potsdam
- Ulm university
- Passau university
- Tu Kaiserslautern
- Tu clausthal
- Btu Cottbus – senffenberg
- Tu Braunschweig
- Magdeburg university
- Technische universität Dresden
- Goethe university frankfurt
- Westfälische Wilhelms-universität münster
- University of cologne
- Universität Jena
6. Which is the easiest German university to get admission into?
According to uscollegeinternational.com, the following universities have the highest acceptance rates:
- Schiller International University – 60%
- Berlin International University of Applied Sciences – 60%
- Ludwig-Maximillian University – 55%
- University of Freiburg – 33%
- University of Heidelberg – 15%
- Free University of Berlin – 15%
- University of Leipzig – 10%
7. What are the requirements to study in Germany? What documents are required to apply for masters in Germany?
To pursue Master’s study in Germany you have to have an Undergraduate degree from an accredited university. Because admissions is competitive, students will be screened for academic performance and adequate preparation to succeed in a rigorous academic curriculum evidenced by higher grades. Students are expected to submit semester mark sheets for all courses completed.
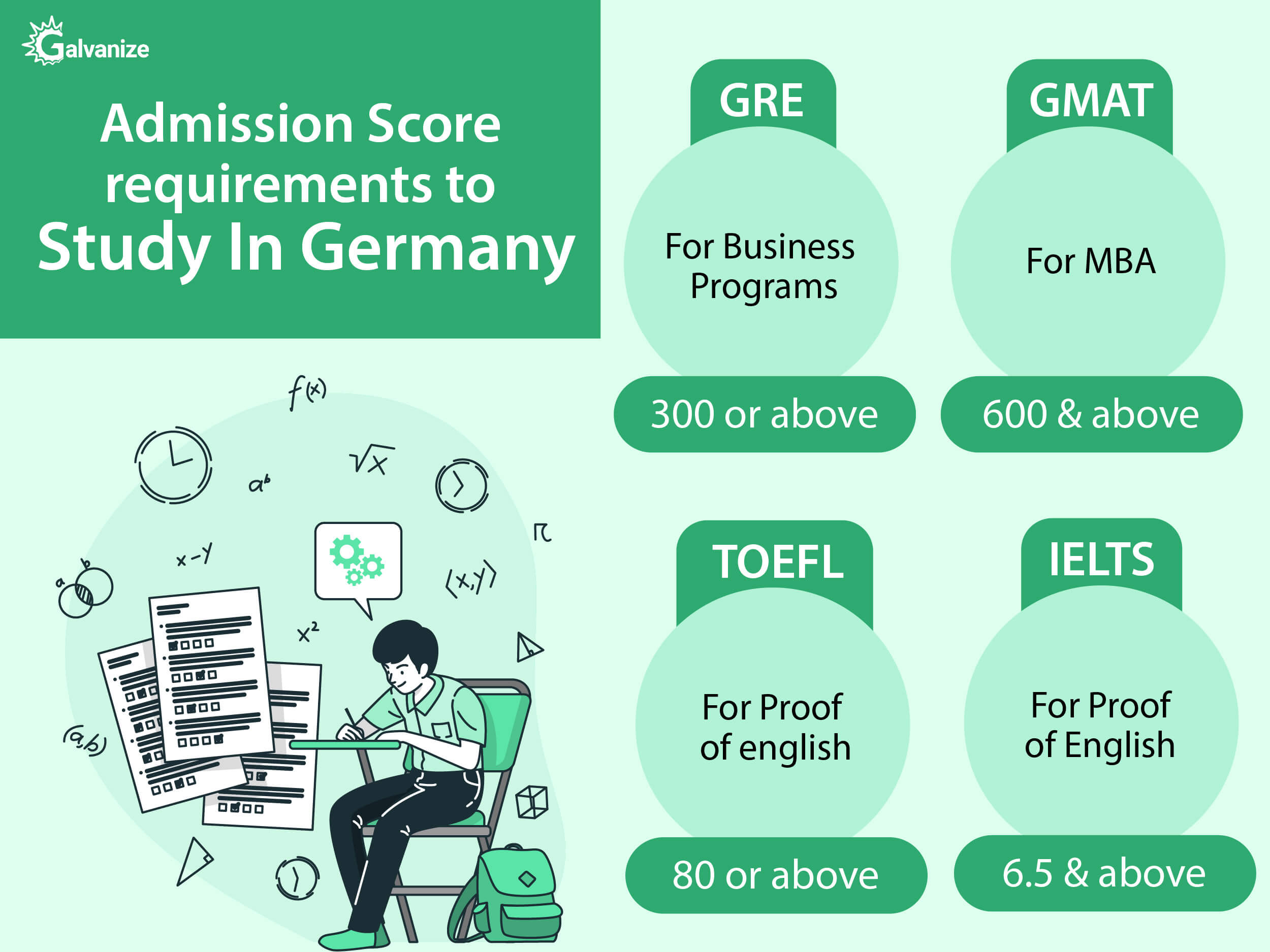
Test Scores:
For most MS programs the GRE is not required, but business programs will require the GMAT/GRE. At Galvanize, we typically recommend programs that are taught in English and to meet the eligibility requirements, it is recommended that students show proof of English Language Proficiency through TOEFL/IELTS.
Other documents requirements:
- Statement of Purpose
- Letters of Recommendation, Official preferred
- Resume
- Valid Passport
8. Is GRE and IELTS or TOEFL mandatory for master’s programs in Germany? - Can I study in Germany without the IELTS?
The GRE is not mandatory for most MS programs. But there are some MS programs that may require it, and also business programs that will accept the GRE in lieu of the GMAT. If a GRE score is required, a score of 300 and above could be considered.
Many MBA programs require the GMAT scores and you could apply to schools with a GMAT score of 600 and above.
Students are required to prove their English proficiency to meet the entrance requirements for programs that are taught in the English Language. To meet english proficiency requirements, we recommend a TOEFL score of 80 and above or IELTS score of 6.5 and above as the expected standard to apply to German universities for graduate studies.
9. What is the minimum CGPA required for MS in Germany?
Since admissions to graduate programs are very competitive due to highly acclaimed international degrees at a low cost to students, A cumulative grade of 70% and above will be considered competitive for graduate program admissions in Germany.
10. Is German language mandatory to study in German universities?
For Undergraduate (UG) admissions, since most UG courses in Germany are taught in the German language, proficiency is required. Undergraduate applicants should prove German language knowledge of level C1 or C2 of the “Common European framework of references for languages”.
For Graduate admissions, since we recommend only programs that are taught in English, students must prove only English language proficiency. But if you plan to live and work in Germany for some time, it will be good for students to consider improving their German language skills.
11. How much funds are required to study a master's in Germany?
For living expenses, students will open a blocked account and show availability of 853 Euros for one month/ 10236 Euros for one year. The living expenses typically cover Rent, food, transportation, leisure activities etc
As for tuition cost, according to the Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD), “The majority of higher education institutions in Germany are financed by the state. There are generally no fees for Bachelor’s courses or most Master’s courses at state higher education institutions. Tuition fees may have to be paid for certain continuing education Master’s programmes, but they are not particularly high compared to other countries. Private higher education institutions may demand more substantial fees for their degree programmes.”
Chapter 4 : Cost & Scholarships | Study In Germany
Table of Contents
1. What is the cost of pursuing undergraduate in Germany?
2. What is the cost of pursuing an MBA in Germany?
3. What is the cost of pursuing a PhD in Germany?
4. How to fund my education in Germany?
5. What are the scholarships available for International Students in Germany?
6. How to apply for the DAAD Scholarship in Germany?
7. How to get a full scholarship for a master’s degree in Germany? / How to apply for a scholarship for studying in Germany?
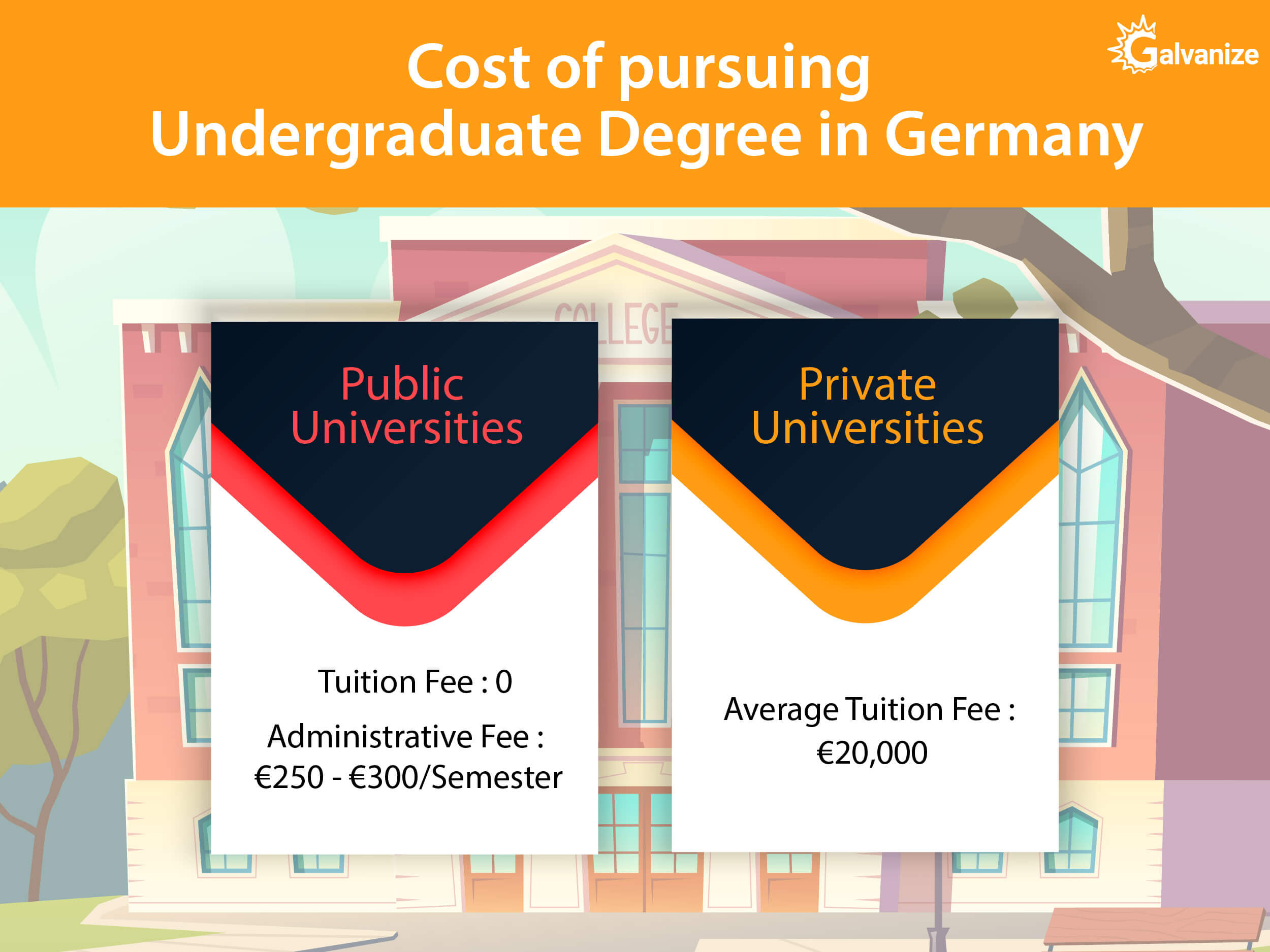
1) What is the cost of pursuing undergraduate in Germany?
- Though undergraduate programs at public universities have free tuition, you will have to pay around €250 – €300 per semester to cover administration costs. There may be an additional fee if you request the Semester ticket, which allows you free use of all public transportation services, but the exact price depends on which Semester ticket option you choose.
- However, if you choose to study in a private university, you will have to pay the tuition fees, though it is significantly less than that of programs in other countries. The average fee for an undergraduate course is around €20,000, though this cost can vary, depending on the program.
2. What is the cost of pursuing an MBA in Germany?
Internationally MBA courses tend to be the most expensive. The traditional MBA course in Germany takes 2 years to complete and can include internships. Since MBAs are non-consecutive Master’s programs, universities in Germany are allowed to charge tuition fees. The cost of an MBA degree in Germany varies largely between public and private universities. On average, tuition cost for Full-time MBA programs range from €30,000 to €50,000, while for Executive MBA courses may amount to around €90,000.
3. What is the cost of pursuing a PhD in Germany?
Apart from the semester fee, a doctorate program in Germany is free for the first three years. If it takes you longer than that to complete your program, you will have to pay the tuition fee for that extra time. However, if your program is only for three years or if you have a scholarship, then you do not need to worry about this.

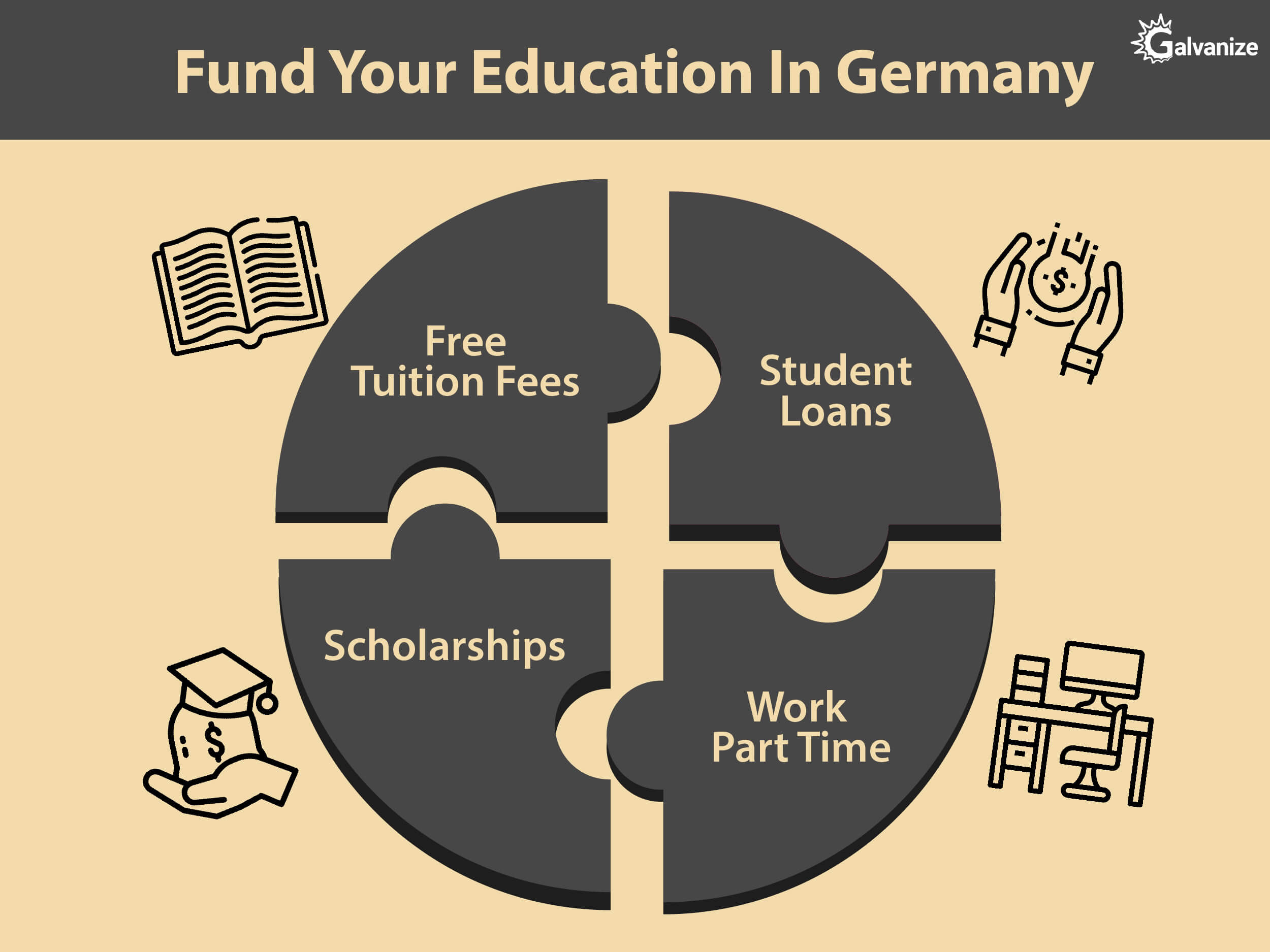
4. How to fund my education in Germany?
Free tuition:
Most German universities offer free tuition for Bachelor’s, consecutive master’s and PhD programs, and students are only required to pay a small fee to cover administration costs.
Scholarships:
There are also several scholarships available for international students, to help ease their financial burden while pursuing their higher education in the country. Please refer to the scholarship for study in Germany section for more information.
Student Loans:
The country also offers student loans, due to the large population of international students that it attracts each year.
Work Part-time:
You can work for 120 full days or 240 half days per year. However, if you take up a job as a research assistant or a teaching assistant, this limit doesn’t apply, but you will need to notify the Foreign Registration Office. Mandatory internships as part of your curriculum are also not included in this limit, but any other internship is considered as work, and the days are subtracted from your limit.
5. What are the scholarships available for International Students in Germany?
There are about 6000 scholarships available in Germany for native and international students. Most of these scholarships not only cover the minimal tuition costs but also help support the student’s living expenses. The most prominent scholarships are:
1. DAAD
The Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst or the German Academic Exchange Service is a government-funded, private organization that provides scholarships for both national and international students. It especially aims at providing scholarships to students from developing countries.
2. Heinrich Böll Scholarships for International Students :
This scholarship is awarded to meritorious students who show a strong interest in environmental and societal issues. Around 1,200 scholarships are awarded each year for students who wish to pursue any type of university degree, as long as they do so in a state-recognized university in Germany.
3. Deutschlandstipendium
These scholarships are provided by universities to exceptional national and international students. Along with academic achievement, extra-curricular and personal achievements are also considered in choosing worthy students.
4. Erasmus Scholarships :
These scholarships are awarded to students from the member states of the European Union who are applying for their master’s. There are two categories of scholarships. Category A scholarships are awarded to students who are not from a European country and have not lived, studied, or worked in any of these countries for more than 12 months. Category B scholarships are awarded to European master’s students.
5. Konrad-Adenauer-Stiftung (KAS) Scholarship :
This scholarship is offered to both MS and Ph.D. students, who are below the age of 30 years. The scholarship is offered for one year, and applicants are required to be skilled in the German language, with at least a level 2 CEFR. This requirement applies even if the course of study you are applying for is taught in English.
6. Humboldt Research Fellowship :
This fellowship is offered to postdoctoral researchers who wish to carry out long-term research for 6-24 months on any topic of their choice, in any institution. This scholarship is awarded to both national and international students.

6. How to apply for the DAAD Scholarship in Germany?
Application procedures vary depending on the scholarship program. Make sure to check out the details pertaining to your program of choice, before applying. However, there are certain steps that are common for DAAD Scholarships:
- Download and fill in the DAAD scholarship application form.
- Download the Europas specimen form and make your CV.
- Get the following documents ready:
- Motivation Letter – This is a letter describing your personality and your reasons for applying for the scholarship. It is required if you are applying for a study scholarship or a grant for a language or specialist course.
- Recommendation letter: Letters from both your previous academic institution and your employer are required.
- Language proficiency: The results of your IELTS is mandatory, as TOEFL is not accepted. If your course of study is taught in German, then proof of your proficiency in German is also required.
- Once you’ve acquired these documents, check if there are any specific documents necessary for the particular scholarship program you are applying for.
- Apply directly to the university.
7. How to apply for a scholarship for studying in Germany?
You can directly apply for scholarships to the university when you are filling in your application. Check to see what scholarships are supported by the institution of your choice.
Chapter 5: Campus Life in Germany | Study In Germany
Table of Contents
1. What is it like to study in Germany for foreign students?
2. What is it like to study at a German university or college? What are the pros and cons of living in Germany?
3. What about the part-time jobs in Germany?
4. How is life in Germany different from the US?
5. What are the employment opportunities in Germany? How do you go about finding a job while you are studying?
6. What jobs can I seek as an international student?
7. What are the transportation options in Germany for international students?
1) What is it like to study in Germany for foreign students?
Germany is a great place for international students. The diverse culture, the safe atmosphere, and of course, the almost free education are all benefits that appeal to international students. The fact that the high standards of teaching and education are maintained consistently across all German universities is also a positive factor. The language barrier, of course, does exist, and most international students choose to study German on the side, to better their prospects of networking and eventually landing a job.
Germany is a beautiful country, with friendly people who are very welcoming to international students. On average, students spend around 850 euros/ month for living expenses in Germany. As such, it is the perfect place for students who wish to gain valuable knowledge and skills in their field, while also building lifelong connections.
2. What is it like to study at a German university or college?
- Firstly, as the tuition cost is low or free for Bachelor’s, Consecutive Master’s and PhD programs. in the majority of universities. Therefore, students who study in Germany don’t have as much financial stress as compared to students who study in other countries. This inevitably allows them to focus on their education and make the most of their stay in the country.
- German universities wish for their students to be independent and expect them to prioritize their studies as required. Moreover, the curriculum is structured in such a manner that it addresses and deals with current issues and trends in the industry. As such, students are able to apply their learning to current-scenarios, which helps ease their shift to the workforce. Moreover, German universities are equipped with great facilities for research and development, which also helps students gain valuable industry-related skills and knowledge.
- As a student, you will probably be living in a hall of residence with your fellow students. However, if accommodation is not available for you on-campus, the universities are more than willing to help you find an affordable place. Living conditions are also great for students, and since you don’t have to pay much for your tuition, you can invest your money in living costs and leisure activities.
- Travel and transport in Germany are easy. The public transport system is excellent as most universities will include a Semesterticket as part of your fees, allowing you free travel within the city. Also, as Germany is bordered by so many other countries, it is simple to cross the border for a weekend holiday, especially as travel to nearby European countries is free and doesn’t require a visa.
- Language can bring people together or divide them. While your courses are taught in English, it would be easier for international students to socialize and network if they are familiar with the German language. Germans are very proud of their language, just like most cultures, and as such, it would be nice to show that you respect it.
3. What about the part-time jobs in Germany?
- Many international students, if they are not on scholarships or just wish to gain some experience, work part-time.
- An international student is allowed to work for 120 full days or 240 half days a year. Universities do not allow students to work for more than 20 hours a week during the semester, which means you can take up full-time jobs during your break.
- The student is required to possess a job permit from the Federal Employment Agency and the foreigner’s authority.
- Working within the university campus would be most ideal, due to the flexible work hours and the proximity to your classes. But getting a job on campus can be difficult, due to the high competition.
- Most importantly, abiding by German employment laws is very important. The wages that a student part-timer gets would exempt them from taxes, as it will probably be below 450 euros a month. However, if you are a research associate and are earning more than this amount, you would be required to pay tax.

4. How is life in Germany different from the US?
|
Life in US |
Life in Germany |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. What are the employment opportunities in Germany? How do you go about finding a job while you are studying?
Germany has the lowest unemployment rates in the EU, and if you have a university qualification and a strong grasp of the German language, you have a pretty good chance of finding employment in the country. Moreover, there’s a shortage of skilled professionals in Germany, mainly in the engineering, manufacturing, and healthcare sectors. So if you are planning to gain a degree in a field related to these domains, your chances of finding employment are pretty high.
Most students who study in German prefer to work part-time while they are pursuing their degrees. With a valid work permit, international students are allowed to work for 120 full days or 240 half days a year. Though universities do not allow students to work for more than 20 hours a week during the semester, you can take up full-time jobs during your break.
You can apply for an extension to your residence permit and stay in the country for up to 18 months after graduation, while you seek employment or plan further education. Make sure that you apply for your extension before you graduate, so as to leave enough time for approval. Once you’ve gained employment, you must contact the Immigration Office, show validation of an employment offer, and apply for a residence permit for employment purposes or an EU Blue Card.
The Federal Employment Agency (BA) is the portal to the largest job market in Germany. If you are searching for employment, this should be your starting point. Apart from this, there are also other job sources that you can look into, such as the EURES which is the network of European employment agencies. Many university students prefer to take up jobs on campus, but these are hard to land, due to the high competition.

6. What jobs can I seek as an international student?
It would be best if you could find a job relevant to your major, as this would add to your work experience. But if you are unable to get a job related to your field, there are still several opportunities for international students on-campus and outside.
1.Graduate assistants:
If you are applying for a master’s degree, then you might try to get a position as a graduate assistant. The job role could include supervising the library, leading tutorials or research literature for professors. Not only will this add to your experience, but you will also be able to earn a decent stipend. Moreover, the 120-day restriction does not apply to academic assistants. However, you must follow the rules set by the particular university and gain permission from the Ausländerbehörde (Foreigner’s Registration Office) if you wish to work more hours.
2. English tutors:
Germans are always eager for a chance to learn and practice their English, so English language tutors are always welcome. However, you would need to be extremely proficient in the language to qualify, especially if you hail from a non-English speaking country.
You may be eligible for other temp jobs. Please contact your university student services to identify legitimate job opportunities. If you choose to be employed as a student, please follow the international student labour regulations.
7. What are the transportation options in Germany for international students?
German cities are built quite close-knit, which means that your basic destinations are at walking distance or at least at biking distance. Besides, insurance and fuel costs in Germany are quite high, so most people prefer to walk or use public transport.
The public transportation system, which includes the Bus, Train (Bahn), Tram (S-Bahn), and Underground (U-Bahn), is also excellent. If your accommodation is a bit far from your campus or if you wish to travel around your region and explore, you might consider investing in a Semesterticket. They are relatively cheap and allow you to freely use public transport within a certain region. However, even without the Semesterticket, students are allowed to travel for free after 7.00 p.m. on weekdays and the whole day on weekends and public holidays. So you might want to consider your living arrangements before investing in a ticket.
Related Blogs
- One Stop Shop : Scholarships for Indian Students
- The Definitive Guide : Statement of Purpose
- A Complete Guide to Study Abroad
- Study In Canada : All about Eligibility, Requirements, Documents, Campus Life, Job Opportunities
- Why Students Prefer Galvanize Admission Counselling
- Study in USA (Complete Guide)



















Thank you for useful article. You have given very good information.